Introduction
Salesforce is a cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) platform that helps businesses of all sizes manage their customer interactions, sales, and marketing activities.
One of the key features of Salesforce is its REST API, which allows developers to interact with the platform’s data and functionality using a variety of programming languages and tools. While the Salesforce REST API is primarily designed for developers, it can also be a valuable tool for business users who want to improve their productivity, automate their workflows, and integrate Salesforce with other systems and applications.
In this article, we will provide an overview of Salesforce REST API endpoints and their benefits for business users. We will explain what REST API endpoints are, how they can be used to access different types of data in Salesforce, and what best practices should be followed when using REST API endpoints. We will also provide examples of how business users can use REST API endpoints to improve their workflows and automate their tasks.
Why Salesforce Introduced REST API Endpoint
When Salesforce first launched, the only way to access data was by logging into the web interface and manually working with records. This worked in the early days, but as businesses grew and technology evolved, the approach quickly became limiting.
Organizations weren’t just using Salesforce anymore , they were relying on dozens of interconnected systems that needed to:
- Share information seamlessly
- Exchange data in real time
- Support custom solutions beyond what the standard Salesforce interface could offer
To address these challenges, Salesforce introduced the REST API Endpoint. The idea was simple: give businesses a programmatic way to access Salesforce data from anywhere, using any modern programming language.
This opened the door to automation, third-party integrations, mobile applications, and business intelligence dashboards that could all consume Salesforce data without manual effort.
Want to explore how Salesforce integrations create real business impact? Checkout the article: What Is Integration? 5 Big Benefits of Salesforce Integration.
Key Concepts of Salesforce REST API Endpoint
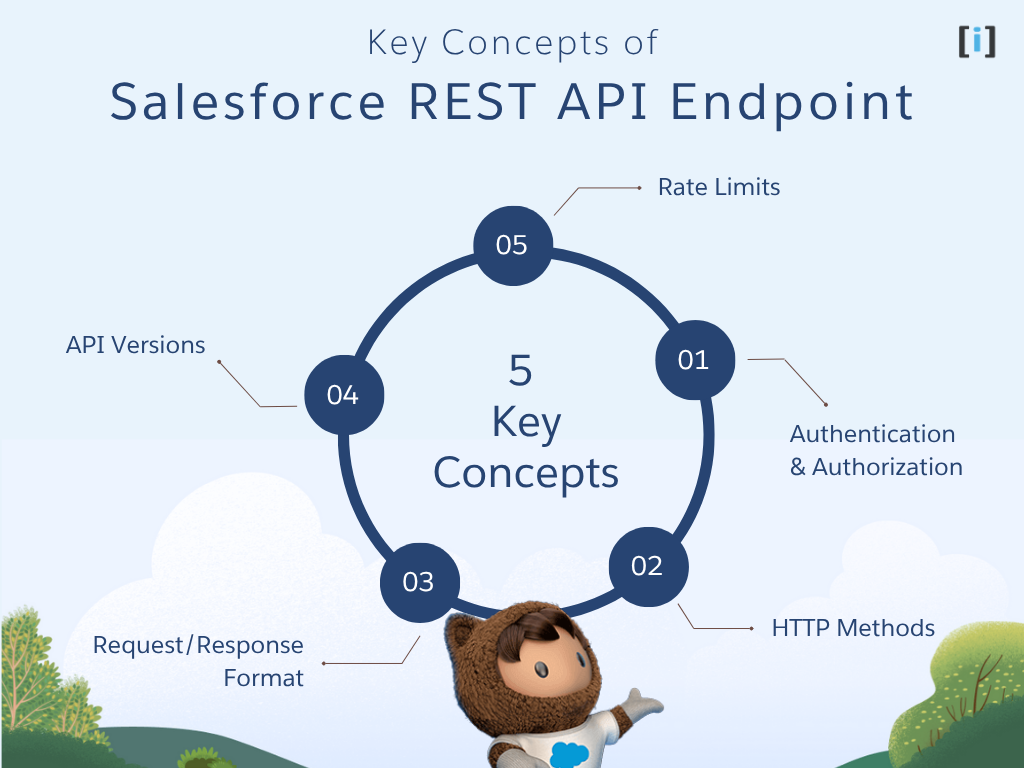
Before diving into usage, it’s essential to understand the fundamental building blocks that make Salesforce REST API work.
Authentication & Authorization
You can’t just “walk in” and request Salesforce data. First, you must prove who you are. Salesforce uses OAuth 2.0, similar to a secure digital keycard system.
- After successful authentication, Salesforce issues an access token.
- Think of this token as a temporary pass: “Yes, this person or system is allowed here.”
- Every subsequent request carries this token to validate identity and permissions.
HTTP Methods
Salesforce REST API Endpoint follows the standard HTTP verbs that most developers already know:
- GET: When you want to read or retrieve data, you use GET.
- POST: This is for creating new records.
- PATCH: When you need to update existing records,
- DELETE: This removes records you no longer need.
Request/Response Format
Communication between external systems and Salesforce REST API Endpoint happens in JSON (JavaScript Object Notation).
- JSON is lightweight, easy to parse, and widely supported.
- It’s designed to be human-readable and machine-friendly.
Example response snippet:
{
"Id": "0015g00000ABC123",
"Name": "Acme Corporation",
"Industry": "Manufacturing"
}API Versions
Salesforce is constantly evolving, adding new features and improving existing ones. That’s why REST API Endpoint uses versions (like v58.0 or v59.0). When the system make a request, they specify which version they’re using.
Rate Limits
Salesforce protects its infrastructure by enforcing API call limits.
- Each org is allocated a specific number of API calls per 24 hours, based on its edition and licenses.
- If you exceed the limit, further requests will be blocked until the limit resets.
It’s important to design your integrations with these limits in mind, using bulk operations when possible and caching data when it makes sense.
Explore How to Find Your Salesforce Edition.
Understanding Salesforce REST API Endpoints
Salesforce REST API endpoints are URLs that allow you to interact with the Salesforce platform’s data and functionality using the REST (Representational State Transfer) protocol. When you make a request to a REST API endpoint, you are sending a message to the Salesforce server asking it to perform a specific action, such as creating a new record or retrieving data from a specific object.
REST API endpoints can be used to access a wide range of data in Salesforce, including standard and custom objects, fields, relationships, metadata, and more. Some common examples of data that can be accessed through REST API endpoints include:
- Account and Contact data
- Opportunity data
- Custom object data
- User and Group data
- Chatter data
REST API endpoints can be used to support a variety of business processes, including:
Sales and Marketing
REST API endpoints can be used to retrieve and analyze customer data, create leads and opportunities, and track sales activity.
Customer Support
REST API endpoints can be used to access customer service data, create and update support cases, and track support activity.
Business Intelligence
REST API endpoints can be used to retrieve and analyze business data, such as sales trends, customer demographics, and marketing campaign performance.
Overall, REST API endpoints can be a powerful tool for business users who want to access Salesforce data in real-time, automate their workflows, and integrate Salesforce with other systems and applications. In the next section, we will explore some of the most common Salesforce REST API endpoints and how they can be used to support business processes.
How to Use Salesforce REST API Endpoint
Now that you understand what Salesforce REST API endpoints are, let’s look at how to actually use them in practice.
Types of Endpoints
Salesforce provides two main categories of endpoints to meet different integration needs:
Standard Endpoints
These are the built-in endpoints that Salesforce provides out of the box. Every Salesforce org can use them to:
- Create, read, update, or delete records (CRUD)
- Run queries with SOQL
- Search across objects
- Access metadata and Chatter feeds
They cover most common business scenarios and require no extra setup.
Custom Endpoints
Sometimes, standard endpoints aren’t enough for unique business requirements. That’s where custom endpoints come in. Using Apex REST services, you can define your own endpoints with custom logic.
Custom endpoints are powerful because they allow you to:
- Combine data from multiple objects in a single response
- Apply complex calculations or business rules before returning data
- Build specialized workflows tailored to your company’s processes
Need expert help? Take a look at this guide on how to quickly hire a Salesforce developer, the right developer can help you design and implement custom endpoints that fit your business needs perfectly.
Working with Endpoints
Using Salesforce REST API endpoint involves a simple 3-step workflow:
Set Up Your Connection
Before making requests, you need to authenticate with Salesforce.
- Typically done via OAuth 2.0, which returns an access token.
- This token must be included in the header of every request.
- Most programming languages and integration platforms (like Postman, MuleSoft, or Workato) provide ready-made libraries to handle this.
Choose Your Action
Decide what you want to do:
- Retrieve data (GET)
- Create new data (POST)
- Update records (PATCH)
- Delete records (DELETE)
Handle the Response
Salesforce responds in JSON format, making it easy to parse. Always:
- Check for success codes (e.g., 200 OK, 201 Created).
- Look for error messages.
- Implement logging or retry logic for failed requests.
Use standard endpoints for common tasks and custom endpoints when you need business-specific logic.
Common Salesforce REST API Endpoints
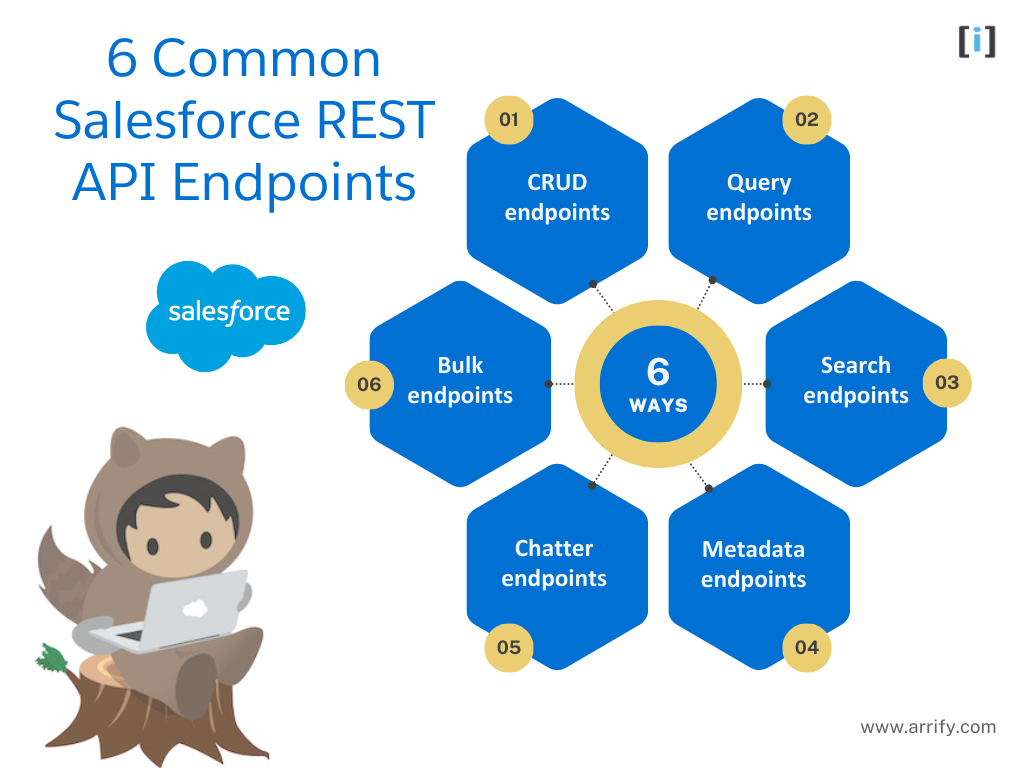
Salesforce REST API endpoints can be used to perform a variety of actions, from creating and updating records to querying and searching for data. In this section, we will explore some of the most common REST API endpoints used in Salesforce and their use cases.
CRUD endpoints
These endpoints allow you to create, read, update, and delete records in Salesforce. Examples of CRUD endpoints include:
- Create : POST /services/data/vXX.X/sobjects/Object__c (creates a new custom object record)
- Read : GET /services/data/vXX.X/sobjects/Object__c/recordId (retrieves a specific record by ID)
- Update : PATCH /services/data/vXX.X/sobjects/Object__c/recordId (updates a specific record by ID)
- Delete : DELETE /services/data/vXX.X/sobjects/Object__c/recordId (deletes a specific record by ID)
Query endpoints
These endpoints allow you to retrieve specific records or sets of records from Salesforce. Examples of query endpoints include:
- GET /services/data/vXX.X/query?q=SELECT+Id,Name+FROM+Object__c (retrieves all records from a custom object)
- GET /services/data/vXX.X/query?q=SELECT+Id,Name+FROM+Object__c+WHERE+Name=’RecordName’ (retrieves a specific record from a custom object)
Search endpoints
These endpoints allow you to search for records based on specific criteria. Examples of search endpoints include:
- GET /services/data/vXX.X/search?q=FIND+{search term} (searches for records across multiple objects based on a search term)
- GET /services/data/vXX.X/sobjects/Object__c/search/?q={search term} (searches for records within a specific custom object based on a search term)
Metadata endpoints
These endpoints allow you to retrieve information about your Salesforce org’s data structure and customizations. Examples of metadata endpoints include:
- GET /services/data/vXX.X/sobjects/ (retrieves a list of all objects in your org)
- GET /services/data/vXX.X/sobjects/Object__c/describe/ (retrieves metadata about a specific custom object)
Chatter endpoints
These endpoints allow you to access and interact with your organization’s Chatter feed. Examples of Chatter endpoints include:
- POST /services/data/vXX.X/chatter/feeds/news/me/feed-items (posts a message to your Chatter feed)
- GET /services/data/vXX.X/chatter/feeds/news/me/feed-items (retrieves your Chatter feed)
Bulk endpoints
These endpoints allow you to perform CRUD and query operations in bulk. Examples of bulk endpoints include:
- POST /services/data/vXX.X/composite/sobjects (creates multiple records in a single request)
- POST /services/data/vXX.X/jobs/ingest (uploads a CSV file to Salesforce and creates or updates records based on the file data)
By using these common REST API endpoints in Salesforce, business users can streamline their workflows, automate their tasks, and integrate Salesforce with other systems and applications. In the next section, we will provide some examples of how REST API endpoints can be used in practice.
Practical Examples of Salesforce REST API Endpoints
Now that we’ve explored some of the most common REST API endpoints in Salesforce, let’s look at some practical examples of how they can be used in real-world scenarios.
Sales Pipeline Management
Suppose you are a sales manager and you want to track the progress of your sales pipeline in real-time. By using the Salesforce REST API endpoints, you can retrieve data about your accounts, opportunities, and leads, and use that information to create reports and dashboards that give you a holistic view of your sales pipeline. For example, you could use the following REST API endpoints:
- GET /services/data/vXX.X/query?q=SELECT+StageName,COUNT(Id)+FROM+Opportunity+GROUP+BY+StageName (retrieves the number of opportunities in each stage of the sales pipeline)
- GET /services/data/vXX.X/query?q=SELECT+Id,Name,Email+FROM+Contact+WHERE+LastModifiedDate>2022-01-01T00:00:00Z (retrieves a list of contacts who were recently updated)
By combining the data from these endpoints with a visualization tool like Tableau or Salesforce’s own Einstein Analytics, you can gain valuable insights into your sales pipeline and make data-driven decisions about how to optimize your sales process.
Customer Support
Suppose you are a customer support agent and you want to quickly access information about a specific customer or support case. By using the Salesforce REST API endpoints, you can retrieve data about your customers, cases, and other support–related objects, and use that information to respond to customer inquiries more efficiently. For example, you could use the following REST API endpoints:
- GET /services/data/vXX.X/query?q=SELECT+Id,Name,Email+FROM+Contact+WHERE+Email=’customer@email.com’ (retrieves a specific customer record by email address)
- GET /services/data/vXX.X/query?q=SELECT+Id,CaseNumber,Subject,Status+FROM+Case+WHERE+ContactId=’contactId’(retrieves a list of support cases associated with a specific customer)
By integrating these endpoints with a customer support tool like Salesforce Service Cloud or a third–party solution like Zendesk, you can provide faster and more personalized support to your customers.
Marketing Automation
Suppose you are a marketing manager and you want to automate your marketing campaigns based on customer behavior. By using the Salesforce REST API endpoints, you can retrieve data about your leads, campaigns, and other marketing-related objects, and use that information to trigger automated marketing workflows. For example, you could use the following REST API endpoints:
- GET /services/data/vXX.X/query?q=SELECT+Id,FirstName,LastName,Email+FROM+Lead+WHERE+IsConverted=false+AND+Status=’Open’ (retrieves a list of open leads that have not been converted)
- POST /services/data/vXX.X/composite/sobjects (creates a new campaign member record and associates it with a specific campaign)
By combining these endpoints with a marketing automation tool like Salesforce Marketing Cloud or a third-party solution like HubSpot, you can create more targeted and effective marketing campaigns that drive engagement and revenue.
Overall, the Salesforce REST API endpoints provide a powerful way for business users to access and manipulate Salesforce data, automate their workflows, and integrate Salesforce with other systems and applications. By learning how to use these endpoints effectively, you can unlock the full potential of the Salesforce platform and drive your business forward.
Best Practices for Working with Salesforce REST API Endpoints
While working with Salesforce REST API endpoints can be a powerful tool for business users, it’s important to follow best practices to ensure that you’re using them effectively and securely. Here are some key tips to keep in mind:
Understand Data Security
Salesforce provides robust data security features, such as object-level and field-level security, to control who can access and modify data. When using REST API endpoints, it’s important to ensure that you’re only retrieving or updating data that you’re authorized to access. You should also be aware of any data privacy regulations that apply to your industry or region, such as GDPR or CCPA.
Use Pagination
Some REST API endpoints can return large amounts of data, which can be slow to process and consume a lot of system resources. To avoid this, use pagination to break up large responses into smaller, more manageable chunks. For example, you can use the “offset” and “limit” parameters to retrieve a certain number of records at a time, or use the “nextRecordsUrl” field in the response to retrieve the next set of records.
Implement Error Handling
REST API endpoints can return various types of errors, such as authentication errors, invalid request errors, or server errors. To handle these errors effectively, you should implement error handling logic in your application, such as retrying failed requests, logging error messages, and providing informative error messages to the user.
Consider Caching
If you’re retrieving data that doesn’t change frequently, such as reference data or lookup tables, consider caching the data in your application to avoid unnecessary API calls. You can use tools like Redis or Memcached to cache data in memory, or use a content delivery network (CDN) to cache data on the network.
Monitor API Usage
It’s important to monitor your usage of REST API endpoints to ensure that you’re staying within your API limits and not causing undue strain on the Salesforce system. You can use tools like Salesforce’s own Event Monitoring or third-party tools like New Relic or Splunk to monitor API usage and performance.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that you’re using Salesforce REST API endpoints effectively and securely, and avoid common pitfalls and issues.
When not to use Salesforce REST API endpoints
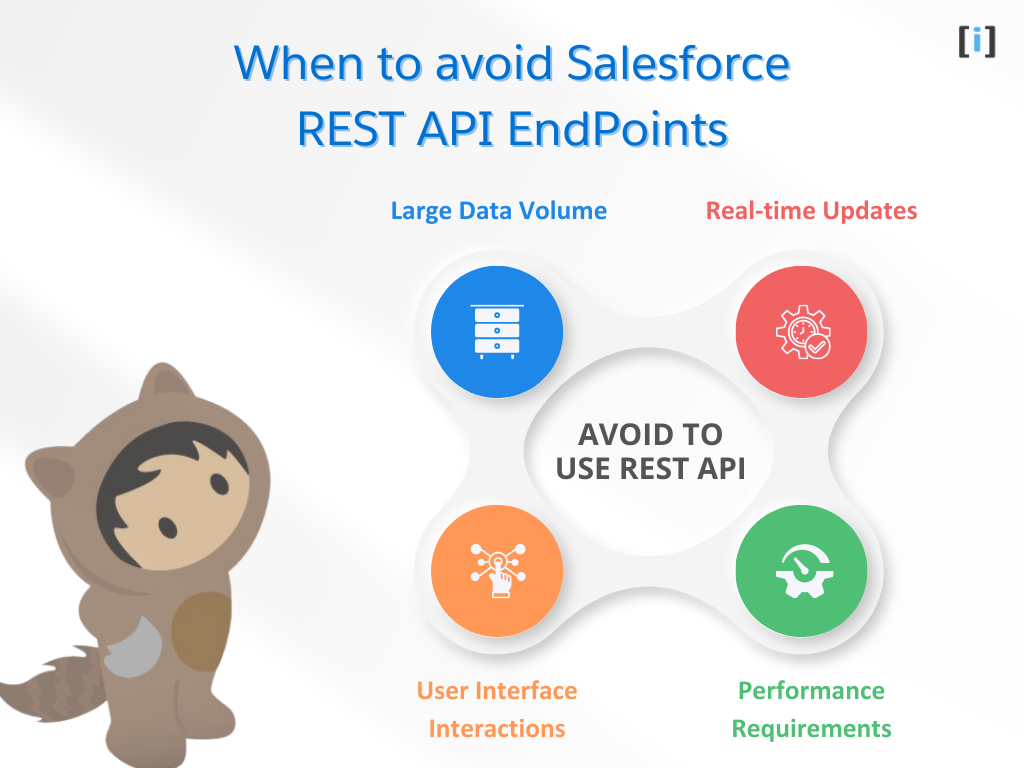
While Salesforce REST API endpoints can be a powerful tool for accessing and interacting with Salesforce data, there are some cases when it may not be the best choice. Here are some scenarios when you may want to consider alternatives to REST API endpoints:
Large Data Volume
If you need to retrieve or update large amounts of data, such as millions of records or large attachments, REST API endpoints may not be the best choice. In these cases, you may want to consider using tools like Bulk API or Data Loader, which are designed to handle large data volumes more efficiently.
Real-time Updates
If you need to receive real-time updates or notifications when data changes in Salesforce, REST API endpoints may not be the best choice. In these cases, you may want to consider using tools like Salesforce Platform Events, Change Data Capture, or Streaming API, which are designed for real-time event-driven architecture.
User Interface Interactions
If you need to interact with Salesforce data through a user interface, such as creating or editing records, REST API endpoints may not be the best choice. In these cases, you may want to consider using Salesforce Lightning Components or Visualforce pages, which are designed for building custom user interfaces.
Performance Requirements
If you have strict performance requirements, such as sub-second response times or high throughput, REST API endpoints may not be the best choice. In these cases, you may want to consider using tools like Apex or Heroku, which provide more fine-grained control over performance and scalability.
By considering these scenarios and evaluating the trade-offs between different tools and technologies, you can choose the best approach for your specific use case and business requirements.
Conclusion
Salesforce REST API endpoints provide a powerful way for business users to access and interact with Salesforce data, whether through custom-built applications, integrations with third-party tools, or simple data queries. By understanding the basics of REST API endpoints, the types of data they can access, and best practices for working with them, you can unlock the full potential of Salesforce and streamline your business processes.
Remember to always follow best practices when working with REST API endpoints, such as understanding data security, using pagination, implementing error handling, considering caching, and monitoring API usage. Additionally, stay up to date with the latest developments and updates to Salesforce REST API endpoints, as new features and improvements are regularly released.
With these tips and tools, you can make the most of Salesforce REST API endpoints and take your business to the next level.
FAQs
How do I authenticate with Salesforce REST API Endpoint?
Salesforce uses OAuth 2.0 as the primary authentication method.
After authenticating, you receive an access token, which must be included in every API request.
For simpler integrations, Salesforce also supports Session ID authentication, but OAuth is recommended for security.
What are the API limits in Salesforce?
Salesforce enforces daily API request limits to ensure fair usage. The exact number depends on your edition and licenses (e.g., Enterprise Edition typically allows 15,000 calls per 24 hours per user license).
What tools can I use to test Salesforce REST API Endpoint?
Postman (most popular for testing API calls)
Salesforce Workbench (Salesforce-provided tool)
